Cold brew coffee has been experiencing a resurgence in popularity due to its distinct flavor profile and smoothness.
In this article, we will delve into the origins of cold brew, the science behind the extraction process, and how to brew the perfect batch at home.
From recognizing the flavor differences between hot coffee and cold brew to discovering the health benefits of this trendy beverage, we will provide you with all the information needed to fully enjoy and appreciate the art of cold brew coffee.
So grab a glass and let’s explore the world of cold brew coffee!
Key Takeaways:
- Cold extraction unlocks unique flavors in coffee by offering a smooth and less acidic taste compared to hot coffee. This is because the cold brewing process extracts fewer oils and acids, resulting in a smoother and sweeter taste.
- Cold brewing is a scientifically-proven method of coffee extraction, with research showing that it can produce a higher caffeine content and smoother taste compared to hot coffee. It also allows for more control over the flavor profile of the coffee.
- When making cold brew, the selection of coffee beans is crucial in achieving the desired flavor profile. Lighter roasts are recommended for a sweeter taste, while darker roasts can provide a more intense flavor. Experimentation is key to finding the perfect bean for your cold brew.
The Renaissance of Cold Brew
The Renaissance of Cold Brew represents a significant shift in the coffee industry, ushering in a new era of flavor exploration and brewing techniques that delve into the intricate chemistry of coffee beans.
In recent years, Cold Brew has gained immense popularity due to its smooth, low-acidic flavor profile, capturing the taste buds of coffee enthusiasts worldwide. The emergence of this brewing method has not only revolutionized how coffee is enjoyed but has also led to a surge in creative innovations. Bean characteristics play a crucial role in Cold Brew, with different varieties yielding distinct flavors and complexities when subjected to varying brewing methods and temperatures.
Introduction to Cold Extraction
Cold Extraction, particularly in the context of Cold Brew coffee, involves the meticulous process of extracting flavors and aromatics from coffee beans through a unique cold brewing method.
This method differs from traditional hot brewing techniques by utilizing cold water for an extended duration, typically 12-24 hours, to slowly extract compounds from the coffee grounds. The cold temperature inhibits the extraction of certain bitter oils and fatty acids, resulting in a smoother and less acidic brew. Water plays a crucial role in the extraction process, facilitating the dissolution of solubles such as caffeine, organic acids, and sugars from the coffee beans.
This gentle extraction process allows for a nuanced development of flavors, often resulting in a sweeter, less bitter coffee profile with subtle undertones.
Unlocking Unique Flavors through Cold Extraction
Cold Extraction opens the door to unlocking unique flavors in coffee, emphasizing the interplay of aromatic compounds, distinct tastes, and the noticeable difference in flavor profiles compared to traditional brewing methods.
The process of Cold Extraction involves a prolonged steeping period, typically ranging from 12 to 24 hours. During this time, the coffee grounds release their soluble compounds slowly, resulting in a smoother and less acidic brew. This slow extraction allows for the development of a wide array of aromatic compounds, contributing to a more complex flavor profile.
Understanding Cold Brew
To truly understand Cold Brew, one must delve into its origins, unravel the complexities of its flavor profile, and discern the stark differences between hot coffee and cold brew creations.
Beginning with its historical evolution, Cold Brew can be traced back to 17th-century Japan, where Dutch traders introduced the method of steeping coffee grounds in cold water to create a refreshing drink.
The flavor characteristics of Cold Brew are distinctly smoother and less acidic than hot coffee, owing to the extended steeping time and low extraction temperature, resulting in a mellow yet bold taste.
In contrast, hot coffee tends to have a more pronounced bitterness and brightness due to the quick extraction process with hot water, producing a different sensory experience.
Origins of Cold Brew
The Origins of Cold Brew can be traced back to the ingenious methods of Dutch traders and the rich history of global coffee trade, culminating in the emergence of unique cold brew variations like the revered Kyoto-style coffee.
Cold Brew, as we know it today, has roots that go deep into the annals of history. It all began with the Dutch traders who sought innovative ways to preserve and transport coffee beans during their voyages across the seas. By steeping coarse-ground coffee in cold water for an extended period, they discovered a smoother, less acidic brew that was not only convenient but also delicious.
This technique revolutionized the coffee industry, eventually becoming a beloved drink enjoyed worldwide. The global coffee commerce played a crucial role in spreading the popularity of Cold Brew, with various cultures incorporating their own unique twists to this refreshing beverage.
Differences in Flavor Profile: Hot Coffee vs. Cold Brew
An intriguing exploration into the Differences in Flavor Profile between Hot Coffee and Cold Brew reveals the nuanced interplay of coffee beans, flavor complexities, and taste perceptions unique to each brewing method.
In terms of hot coffee, the brewing process often accentuates the bold, robust characteristics of the beans. The heat extracts oils and acids more rapidly, resulting in a richer, more intense flavor profile.
On the other hand, cold brew, with its extended steeping time in cold water, tends to bring out the sweeter, smoother notes of the beans, offering a milder and less acidic taste experience.
The Science Behind Cold Brew
Unraveling The Science Behind Cold Brew unveils the intricate chemistry of coffee, the caffeine dynamics, the smooth texture, and the delicate balance of acidity within the complex interplay of chemical reactions and flavor compounds.
This cold brewing method allows for a slower extraction process compared to hot brewing, resulting in a different chemical profile. During cold brew preparation, caffeine extraction occurs at a lower rate due to reduced solubility at lower temperatures, leading to a beverage that is generally less bitter but still rich in caffeine content. The gradual steeping of ground coffee in cold water facilitates the release of flavorful oils and compounds, contributing to the well-rounded taste and smooth mouthfeel associated with cold brew.
Exploring Caffeine Extraction in Cold Brew
Delve into the Intricate Process of Caffeine Extraction in Cold Brew, unraveling the unique methodologies, bean selection intricacies, and the precise extraction processes that define the caffeine content in cold-brewed coffee.
In terms of the extraction techniques used in cold brew, the most common methods involve steeping coarsely ground coffee beans in cold water for an extended period, typically around 12-24 hours. This slow extraction process allows the caffeine and other compounds to dissolve gradually, resulting in a smoother, less acidic brew compared to traditional hot brewing methods.
Bean sourcing is a critical factor that influences caffeine levels in cold brew. Choosing high-quality, freshly roasted beans with a medium to dark roast profile is often recommended for cold brewing. These beans contain the right balance of oils and compounds that contribute to a rich flavor profile and optimal caffeine extraction.
The impact of different processes on caffeine concentration is significant. Factors such as grind size, water temperature, brewing time, and bean-to-water ratio all play a role in determining the final caffeine content of the cold-brewed coffee. Fine-tuning these variables can result in varying caffeine levels, allowing coffee enthusiasts to customize their brew according to their preferences.
The Smoothness Factor: Science Behind Cold Brew
The Smoothness Factor in Cold Brew is a result of precise scientific principles, the optimal roast profiles, and the intricate chemistry that contribute to the velvety texture and unique sensory experience of cold-brewed coffee.
Roast levels play a crucial role in determining the smoothness of Cold Brew. Lighter roasts provide brighter acidity and more pronounced fruity notes, while dark roasts offer a deeper, richer flavor profile. The scientific processes during roasting lead to the development of caramelization, Maillard reactions, and the breakdown of complex compounds into simpler, more soluble forms.
These compounds, when extracted in cold water over an extended period, result in a brew that is less acidic and rich in flavor. The chemistry involved in cold brewing involves the slow extraction of oils, sugars, and caffeine, producing a smoother, less bitter cup of coffee.
Coffee Bean Selection for Cold Brew
The Critical Aspect of Coffee Bean Selection for Cold Brew plays a pivotal role in defining the aromatic profile, grind size preferences, and the regional origin nuances that contribute to the overall flavor complexity of cold-brewed concoctions.
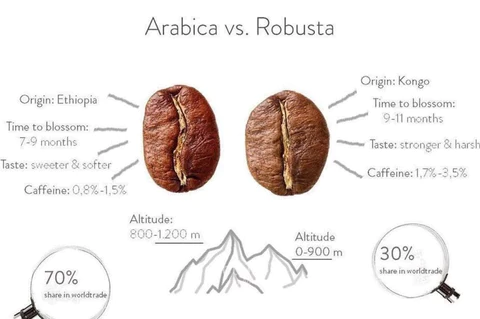
When selecting coffee beans for Cold Brew, it’s crucial to consider the intricate balance between acidity and sweetness, as different bean characteristics can significantly impact the final taste. Origin diversity adds a layer of complexity, with beans from regions like Ethiopia offering fruity and floral notes, while beans from Brazil tend to bring out chocolatey undertones.
Grind size plays a vital role in the brewing process, influencing extraction rates and overall flavor intensity. Coarser grinds are ideal for Cold Brew, allowing for a smoother, less bitter taste.
Understanding these factors can give the power to coffee enthusiasts to craft unique and flavorful cold brew creations at home.
The Cold Brew Process
The Cold Brew Process is a meticulous journey that involves carefully orchestrated steps, varied influencing factors, and the art of brewing that ultimately shapes the distinct flavor profile of this beloved cold-infusion method.
One of the key aspects influencing the flavor development in the Cold Brew Process is the coarseness of the grind. Finely ground coffee beans can result in over-extraction, leading to a bitter taste, while a coarse grind can yield a smoother flavor.
The brewing techniques employed vary from steeping the coffee grounds in cold water for an extended period to utilizing a slow drip method. These different techniques allow for nuanced flavors to develop, creating a range of taste profiles.
The unique taste of cold brew also stems from the process intricacies such as the long brewing time and the absence of heat, which result in a smoother, less acidic beverage that showcases the subtle nuances of the coffee beans.”
Step-by-Step Guide to Cold Brew Brewing
Embark on a Flavorful Journey with this Step-by-Step Guide to Cold Brew Brewing, where every intricate step, every precise measure, and every moment of anticipation culminate in the perfect cup of cold-brewed delight waiting to be savored.
Begin your cold brew adventure by selecting high-quality coarse coffee grounds and filtered water to kickstart the process. Next, combine the grounds and water in a designated brewing container, ensuring a thorough saturation. Let the mixture steep for 12-24 hours, allowing the flavors to develop gradually. Once the steeping time is up, strain the concentrate using a fine-mesh sieve or cheesecloth to separate the liquid from the grounds. The result? A smooth, rich concentrate ready to be diluted with ice, water, or milk, and embellished with your choice of sweeteners or flavorings.
Factors Influencing Cold Brew Flavor
An Exploration of the Multifaceted Factors Influencing Cold Brew Flavor reveals the intricate dance of taste sensations, aromatic notes, and soluble compounds that harmonize in cold-brewed elixirs, creating a symphony of flavors unlike any other.
When diving into the world of cold brew, one must consider the interplay of flavor components, which encompass a broad range of elements such as acidity, sweetness, bitterness, and body. These components, influenced by factors like brewing time, bean origin, and grind size, work together to define the overall taste profile of the cold brew.
The taste influencers further add complexity to the flavor experience, with variables like water quality, temperature, and brewing method impacting how the flavors unfold on the palate. Aromatic nuances play a crucial role as well, with the subtle hints of fruits, flowers, or spices infusing the brew with layers of sensory delight.
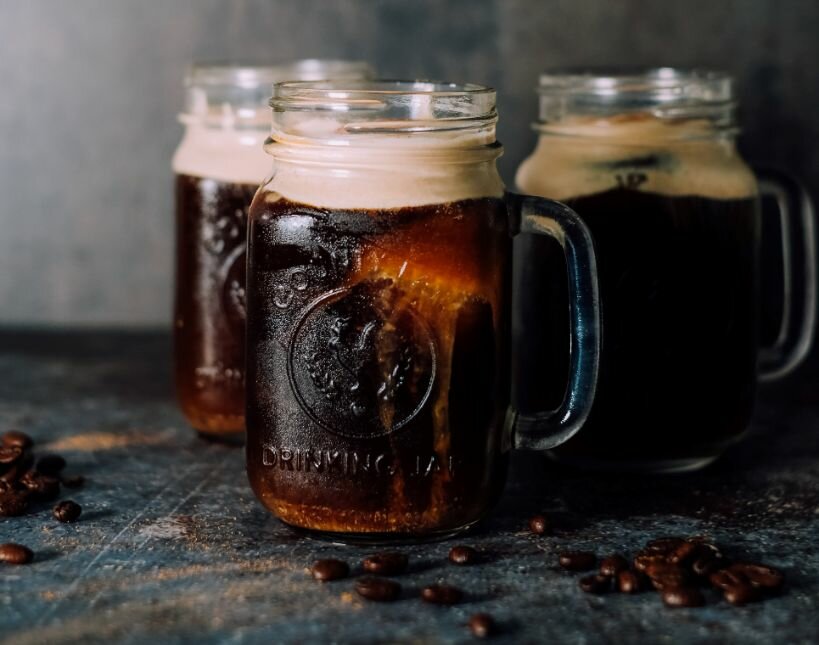
Enjoying Cold Brew
Savoring the Delights of Cold Brew transcends mere consumption; it’s a sensory experience that involves the art of serving, the joy of savoring each sip, and the holistic appreciation of the myriad health benefits that accompany this chilled coffee indulgence.
Cold Brew, with its lower acidity levels and smoother taste profile compared to traditional hot coffee, lends itself to various serving techniques.
- Cold Brew can be served over ice for a refreshing summer treat or even blended with milk or cream for a creamier texture.
- Adding a hint of flavor with syrups or spices can elevate the taste experience further.
The slow steeping process of Cold Brew not only enhances its flavor but also contributes to health perks. For those sensitive to hot brewed coffee’s acidity, Cold Brew is gentler on the stomach and can be a more digestible option.
Tips for Serving and Savoring Cold Brew
Elevate Your Cold Brew Experience with Expert Tips for Serving and Savoring, where each nuanced suggestion, every refined technique, and all the delightful nuances converge to enhance your enjoyment of this refreshing coffee creation.
When presenting your cold brew, opt for clear glassware to showcase its rich color and texture. It’s advised to smell the brew first to capture the initial aromatic notes, then take a small sip to evaluate the flavors. To fully appreciate the complexities, let the cold brew linger on your palate before swallowing. Experiment with serving temperatures to find what best suits your taste preferences. Consider pairing your cold brew with foods that complement its bold yet smooth profile, enhancing the overall experience.
Health Benefits of Cold Brew Coffee
Unveil the Nutritional Secrets and Wellness Wonders of Cold Brew Coffee, where the intricate processes, beneficial reactions, and curated compounds meld to offer a brew that not only delights the senses but also nurtures the body with its array of health advantages.
In particular, the nutritional perks of cold brew coffee stem from its concentrated nature, resulting in higher levels of certain beneficial compounds such as antioxidants and chlorogenic acid. These elements play a vital role in promoting wellness attributes by aiding in the body’s natural detoxification processes and offering protection against oxidative stress. The lower acidity of cold brew coffee makes it a gentler option for individuals with sensitive stomachs, reducing the likelihood of digestive discomfort.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cold extraction and how does it enhance the flavors of cold brew coffee?
Cold extraction is a brewing method that involves steeping coffee grounds in cold or room temperature water for an extended period of time. This slow process allows for a smooth and low-acidity extraction, resulting in a unique and more complex flavor profile.
Why has there been a resurgence in the popularity of cold brew coffee?
Cold brew coffee has gained popularity due to its smooth and less bitter taste compared to traditional hot brewed coffee. Additionally, its lower acidity levels make it easier on the stomach and the slow brewing process allows for a more concentrated coffee flavor.
What makes cold extraction different from hot extraction?
Hot extraction involves brewing coffee with hot water, which can result in a more acidic and bitter taste. Cold extraction, on the other hand, uses cold or room temperature water, resulting in a smoother and less acidic flavor profile.
What are some unique flavors that can be unlocked through cold extraction?
Cold extraction can bring out distinctive flavors in coffee such as fruity, floral, or even chocolate notes. These flavors are often masked in hot brewed coffee but can be highlighted in cold brew due to the longer steeping process.
Can any type of coffee bean be used for cold extraction?
Yes, any type of coffee bean can be used for cold extraction. However, different beans may result in different flavor profiles, so it’s best to experiment with different types to find your preferred taste.
Is cold brew coffee only served cold?
No, cold brew coffee can also be served hot. It can be heated in the microwave or on the stove, or added to hot water, milk, or other hot beverages. However, many people prefer to consume cold brew chilled or over ice for a refreshing and smooth taste.